This section will be available this Autumn.

Galerie Cento Anni
andré lanskoy
André Lanskoy (Moscow 1903-1976 Paris) Un cas suspect, 1964 Oil on canvas 97 x 146 cm Signed and dated 'Lanskoy 64' Provenance: Galerie de Seine; private collection, Paris Certificate of authenticity from the Comité Lanskoy dated 4 April 2025 This work will be included in the forthcoming catalogue raisonné currently in preparation
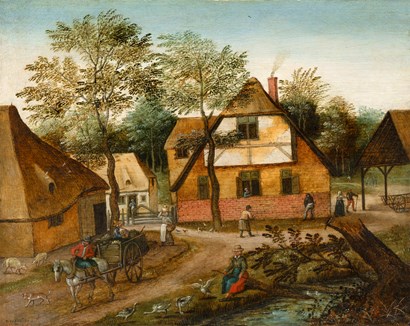
Pelgrims de Bigard
pieter brueghel the younger
Pieter Brueghel the Younger (Brussels 1564-1638 Antwerp) A village scene with a horse-drawn cart and a goose keeper Oil on panel 25 x 31 cm Signed lower left 'P. BREUGHEL' Provenance: collection Kaufmann, before 1934; Kunsthandel P. de Boer, Amsterdam, 1934; collection Van Hees, The Netherlands, until 1969; private collection, The Netherlands Literature: P. de Boer, De Helsche en de Fluweelen Brueghel en hun invloed op de kunst in de Nederlanden, exhibition catalogue, Amsterdam 1934, ill. p. 9, p. 32, n° 32; Pantheon, Monatsschrift für Freunde und Sammler der Kunst, Munich, 1934, XIII, ill. p. 141; P. de Boer, Catalogus van oude schilderijen, exh. cat., Amsterdam, 1940, ill. n° 8; Singer Museum, Modernen van toen 1570-1630, Vlaamse schilderkunst en haar invloed, exhibition catalogue, Laren 1963, n° 53; Georges Marlier, Pierre Brueghel le Jeune, 1969, pp. 417-418, ill. n° 263; Klaus Ertz, Pieter Brueghel der Jüngere (1564-1637/38), die Gemälde mit kritischem Oeuvrekatalog, Lingen 2000, Vol. II, p. 821, ill. n° 667, p. 824, inv. n° E116 Exhibitions: Amsterdam, Kunsthandel P. de Boer, De Helsche en de Fluweelen Brueghel en hun invloed op de kunst in de Nederlanden, 10 February-26 March 1934, n° 32; Amsterdam, Kunsthandel P. de Boer, November-21 December 1940, n° 8; Laren (N.H.), Singer Museum, Modernen van toen 1570-1630, Vlaamse schilderkunst en haar invloed, 15 June-1 September 1963, n° 53

Galerie Capazza
Goudji (Georgia, Bordjomi 1941) Oryx à la robe diaprée, 2025 Silver 1st title, serpentine, pyrite, crystal, Armour stone H 49 x W 38 x D 10 cm Provenance: the artist's studio Exhibition: Goudji, L'or du temps, 5 July-28 September 2025, Galerie Capazza (France) This oryx, with its serpentine goatee and crystal-adorned tail, is an African antelope. It sports horns and a coat draped in Armour stone, and wears a silver bell around its pyrite neck, ready to ring. 'When viewing Goudji's works, one is overcome by a disturbing feeling, that of being faced with original, powerful, dazzling masterpieces that delicately resonate with so many symbols that shape our visual culture and our common heritage, from Persia to Athens, from Babylon to Rome, from the Tigris to the Danube, winged griffins of malachite and lapis lazuli, birds with bold and daring beaks, reassuring ex-votos, kantharoi and cups worthy of banquets of the gods. Modest, always secretive, born into goldsmithing because he ardently wanted to be, constantly devoted to his craft, constantly exploring forms, constantly telling stories, Goudji has definitely entered into history.' by Olivier Gabet, 2025 (General Curator of Heritage and Art Historian - Director of the Department of Decorative Arts at the Louvre Museum)
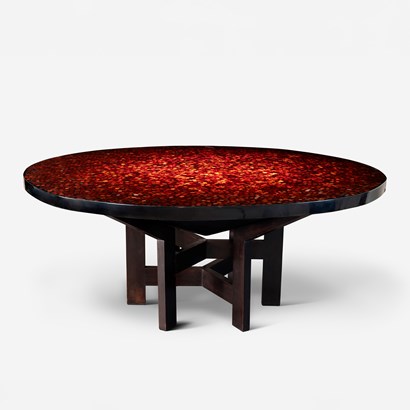

unforget Decorative Arts
ado chale
Ado Chale (Brussels, 1928-2025) Dining table, circa 1970 Resin top inlaid with carnelian agate stones H 71.5 cm - Ø 173 cm This work is accompanied by a certificate of authenticity issued by Ado Chale This table features a backlit tabletop that enhances its sculptural presence and creates a refined play of light and shadow.
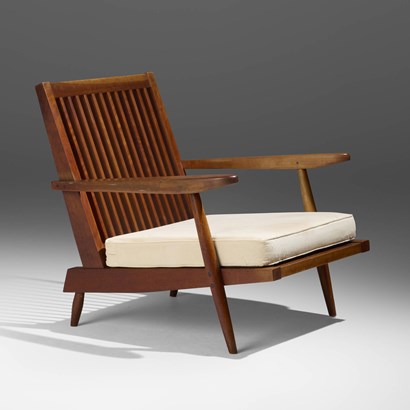

Laurent Schaubroeck
George Nakashima (USA, Washington 1905-1990 Pennsylvenia) Cushion chair with arms, 1960s Black American cherry, upholstery 77.5 x 74.3 x 86.4 cm Produced by George Nakashima Studio Includes a digital copy of the order card Provenance: Craighead family Produced by the Nakashima Studio in the 1960s, this lounge chair exemplifies George Nakashima’s refined craftsmanship and harmony between form and material. Its spindled back recalls Windsor traditions, while the tapered legs and clean geometry express his modern sensibility. Upholstered in white linen, the chair combines warmth and elegance, standing as a rare and timeless piece from one of the most influential American designers of the 20th century.

Galeria Bessa Pereira
Sergio Rodrigues (Rio de Janeiro, 1927–2014) 'Kilin' chair, 1970s Solid wood, leather H 68 x W 68 x D 68 cm Origin: Brasil Provenance: private collection, Rio de Janeiro; Galeria Bessa Pereira collection Literature: Vicente, A., & Vasconcellos, M. (Comps.), Móvel moderno brasileiro (1st edition), São Paulo: Olhares, 2017, p. 302; Cals, S, Sergio Rodrigues, Rio de Janeiro: Icatu, 2000, p. 142

Romigioli Antichità
Pair of marble plates with semi-precious stones and soft polychromes Florence, early 19th century 44 x 38 cm (plates) 62.5 x 55 cm (frames) Provenance: Florentine workshop Oval plate depicting a naturalistic composition with a basket, flower buds, fruit and birds, one with a bird's nest, the other with a nest and eggs, in an antique carved and gilded wooden frame.

Kunsthaus Kende
Pair of George I Britannia silver tea caddies John Farnell, London, 1720 Engraved sterling silver H 12.5 cm 240.3 g and 237.4 g Provenance: private collection, North America The smooth, octagonal body merging into the correspondingly smooth shoulder. The lid finished with a twisted baluster. The base, which can be pulled out for filling, is only marked with a maker’s mark, the lid is unmarked. The bodies are hallmarked on the underside of the back. The contemporary coat of arms engraved on the front commemorates the marriage of a gentleman of the Dove family (who were based in East Burgholt in the county of Suffolk) and a lady of the Pierse family (whose family was based in Alston in the county of Warwickshire). An attractively preserved, early Britannia silver pair of tea caddies with a beautifully preserved, original surface.

Willow Gallery
Bernard Buffet (Paris 1928-1999 Tourtour) Chevalier d'Henri III, 1998 Oil on canvas 130 x 89 cm Signed and dated This painting is sold with a photo-certificate of authenticity from the Galerie Maurice Garnier, Paris Provenance: Galerie Maurice Garnier, Paris; private collection, Germany (acquired from the above 2000); sale, Christie's London, 21 June 2012; private collection, Hong Kong Literature: Y. Le Pichon & M. Garnier, Bernard Buffet, 1982-1999, vol. III, 2007, Switzerland, n° 1261 (ill. p. 552)

Stern Pissarro Gallery
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (Limoges 1841-1919 Cagnes-sur-Mer) Femme dans un paysage, 1917 Oil on canvas 25.3 x 39.7 cm Stamped lower right: Renoir Provenance: the artist's estate; Palais Galliera, Paris, 18 March 1964, (titled 'Gabrielle au jardin'); Hôtel George V, Paris, 10 December 1996, (titled 'Paysage'); private collection, Italy Literature: Marc Elder, L'Atelier de Renoir, vol. II, L'Atelier de Renoir (n.p.: MM. Bernheim-Jeune, Editeurs d'Art, 1931), n° 59 (ill. pl. 187, first state, titled as 'Paysage, bouquet'); Albert André, Marc Elder, and Messrs. Bernheim-Jeune, Renoir's Atelier / L'Atelier de Renoir, Rev. ed. (Paris: MM. Bernheim-Jeune, Éditeurs d'Art, Paris; San Francisco: Alan Wofsy Fine Arts, 1989), n° 599, p. 243 (ill. pl. 187, first state, titled as 'Paysage, bouquet'); Guy-Patrice Dauberville and Michel Dauberville, Renoir: Catalogue raisonné des tableaux, pastels, dessins et aquarelles, vol. V, 1911-1919 (Paris: Éditions Bernheim-Jeune, 2014), no. 3981, p. 204 (ill. p. 204, present state, as "Paysage du Midi") Exhibitions: Paris, Galerie Jean Charpentier, Beautés de la Provence, 17 December 1947-7 March 1948, n° 129 (titled as "Gabrielle au jardin," dated circa 1915) This work is accompanied by letter from the Wildenstein-Plattner Institute confirming the work will be included in the forthcoming Renoir digital catalogue raisonné.
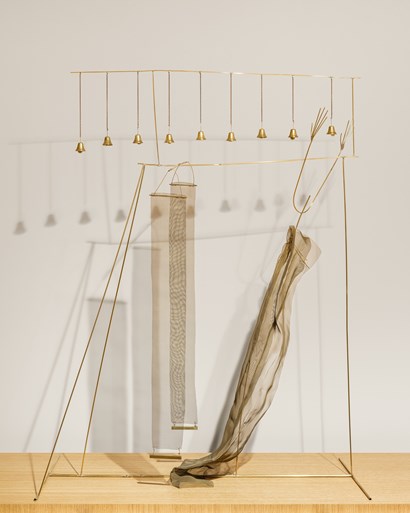

Pron
fausto melotti
Fausto Melotti (Rovereto 1901-1986 Milan) Il meridiano delle campane, 1979 Brass H 97.5 x W 74 x D 38 cm Literature: Milan, Galleria Stendhal, Cascella Consagra Melotti, 1980; Padua, Stevenson Arte Contemporanea, Fausto Melotti. Sculture, tecniche miste e incisioni, 1982; Intra, Galleria Corsini, Fausto Melotti. Sculture e Acquarelli. Un'opera d'arte è un'oasi, 1982; Busto Arsizio, Galleria Il Punto Sette, Fausto Melotti, 1984; Parma, Galleria La Sanseverina, Fausto Melotti, 1986, pp. 29, 47, n° 29, ill. Exhibitions: Gianni Cavazzini, Poetiche sosprese di Fausto Melotti, in Gazzetta di Parma, May 23rd, 1986, ill.; Germano Celant, Melotti, Catalogo generale, Tomo secondo, Sculture 1973-1986 e Bassorilievi, Milan 1996, p. 512, 1979 n° 21, ill.

Galerie Greta Meert
carla accardi
Carla Accardi (Trapani 1924-2014 Rome) Frammenti, 1984 Acrylic on canvas 50 x 60 cm Frammenti, a work from 1984, ‘Fragments’; the work affirms Carla Accardi’s place as a voice of innovation in an Italian art scene dominated by male voices. In this 50 x 60 cm painting using only black paint on the untreated material of the canvas, the artist constructs a rhythmic interplay of signs animating recognition and illegibility, an evocation of a writing that dissolves into abstraction. The work embodies the tension that characterises her oeuvre: a subtle intertwining of classical painterly discipline and the radical openness of the avant-garde, resulting in a visual language that is as rigorous and experimental as it is personal.
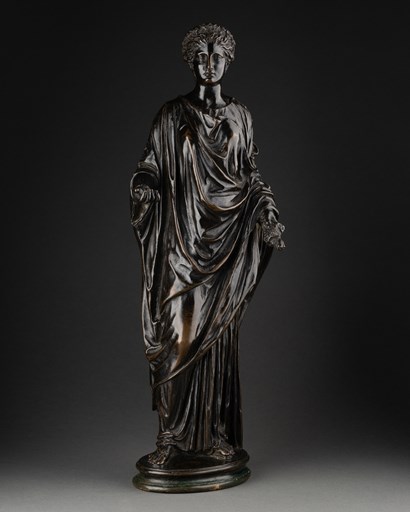

Desmet Fine Arts
giovanni & giacomo zoffoli
Giacomo (Italy, 1731-1785) & Giovanni Zoffoli (Italy, 1745-1805) Capitoline Flora, late 18th century Bronze H 34 x W 10 x D 7 cm Signed 'G.Z.F' (base) After the antique model (Capitoline Musea, Rome) Accompanied by Art Loss Register certificate: S00247973 Other versions: Victoria & Albert: Museum inv. n° A.14-1974; Saltram, National Trust, 871621.4; Philadelphia Museum of Art, Acc # 1978-70-139; Oxford, Ashmolean Museum: Acc # WA1899.CDEF.B449

De Jonckheere
pieter brueghel the younger
Pieter Brueghel the Younger (Brussels 1564-1638 Antwerp) The Payment of the Tithe or the Village Lawyer, 1622 Oil on panel 78.9 x 123.2 cm Signed and dated: P. BREVGHEL, 1622 Provenance: private collection, Belgium; Galerie Legenhoek, Paris, 1991; private collection, France Literature: Ertz, Klaus, Pieter Brueghel der Jüngere: Die Gemälde mit kritischem Oeuvrekatalog, Lingen, Luca Verlag, Vol. I, 2000, p. 513, cat. E 507, repr.; Curie, Christina, Allart, Dominique, The Brue[H]el Phenomenon, Brussels, Royal Institute for Cultural Heritage, vol. III, p. 1030-1031 This Payment of the Tithe, or The Village Lawyer, is marked by Pieter Brueghel the Younger’s verve, meticulous execution, and vibrant colours. The satirical subject mocks the profession of the lawyer responsible for collecting the heavy tax that the poorest peasants struggled to pay. The grotesque faces of the petitioners, as well as the lawyer’s prognathous jaw - associating him with the Spanish authorities then in power - fascinate through their caricatural force. This original composition by Pieter Brueghel the Younger stimulated the market of the time, generating strong demand. The success of this still-relevant satire has endured to the present day.
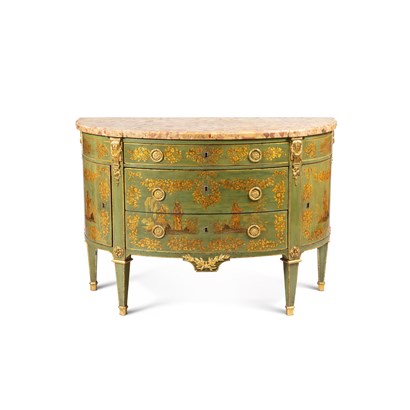

Franck Anelli Fine Art
charles topino
Charles Topino (Arras, circa 1742-1803) Louis XVI period demi-lune commode, circa 1780 Oak, Parisian varnish, gilt-bronze mounts, Aleppo breccia marble top H 91 x W 131 x D 58 cm Stamped 'C. TOPINO' and 'JME', with a CD mark Provenance: private collection, Paris Literature: Forray-Carlier et M. Kopplin, Les secrets de la laque française: Le Vernis Martin, Paris, 2014 This demi-lune commode is decorated with chinoiserie motifs in gold on a green background,. It opens with two side doors and three drawers. The gold chinoiserie decoration on green varnish is quite rare, especially on Louis XVI furniture. The chinoiserie theme is executed here in a decorative style from the 1780s, with framed scenes surrounded by tied garlands. This exotic theme remained in vogue during the Louis XVI period, as evidenced by the lacquered Japanese furniture favoured by Marie-Antoinette, as well as the marquetry furniture by Roentgen. Jean Pillement (1728-1808) popularised chinoiserie designs through his 1776 book 'Œuvres de Fleurs, ornements, cartouches et figures et sujets chinois…etc.,' which spread throughout the courts of Europe. The green varnish décor is especially known for works by René Dubois, such as the small demi-lune commode housed at Waddesdon Manor in England (Inv. WI/23/2). René Dubois, however, was more inclined towards neoclassical scenes, a style that is well-documented in his stock from 1772, which lists around twenty pieces, thus helping to date his production. At this time, the workshop of the Frères Martin was still active, with Jean-Alexandre, the son of Robert Martin, having taken over his father’s workshop in 1767 and acquired that of his cousin Etienne-François in 1772, following his cousin's death the year before. It is clear that Jean-Alexandre benefited from the strong connections his family had with Parisian marchand-merciers and cabinetmakers, one of the most renowned of whom was Charles Topino. This production unfortunately did not survive the French Revolution, and this commode is one of the last examples of this inventive period. Charles Topino settled in Rue du Faubourg Saint-Antoine and counted aristocratic clients and marchand-ébénistes such as Delorme and Tuart amongst his customers. His pieces were described as 'à l'antique,' an expression referring to the neoclassical taste that dominated the late 18th century. His journal, covering the years 1771 to 1779, has survived, providing insight into the names of bronziers who supplied him, including Jean-Baptiste Dubuisson, a master founder since 1765, who created some of the finest bronze mounts of the period. It is known that the gilt bronze mounts adorning Topino’s furniture were cast by Viret, chased by Chamboin and Dubuisson, and gilded by Bécard, Gérard, and Vallet. Charles Topino produced several demi-lune commodes of this type, many decorated with marquetry and several with varnish decorations. Notable examples include: -A commode from the Prince Radziwill collection, sold at the Château d'Ermenonville auction, Ader study, March 8th, 1933 -A writing desk sold by Christie's London from the Rechnitzer collection, May 19th, 1955, illustrated in Connaissance des Arts n° 41, July 15th, 1955 -A writing desk decorated with European black and gold varnish in the Chinese style, sold at Paris’s Hôtel Drouot, Cornette de Saint-Cyr study, January 31st, 1994 -A writing desk with Coromandel lacquer decoration, from the Princess A. de Broglie collection, ill. in P. Verlet, Les ébénistes du XVIIIe siècle français, Connaissance des arts, Hachette, Paris, 1963, p. 268

Galerie Boulakia
Joan Miró (Barcelona 1893-1983 Palma) Des figures devant la lune, 1942 Pastel, gouache, wash, brush, ink, and pencil on paper 64.5 x 48.5 cm Signed 'Joan Miró' (lower right) Dated 'X Barcelone, 18-12-1942' and titled on reverse Certificate of authenticity from ADOM dated 13 July 2018 Provenance: Pierre Matisse Gallery, New York; Galleria Narciso, Turin Exhibitions: Traveling exhibition Japan, 1984, reproduced cat. n° 17; Ferrara, Palais des Diamants, Joan Miró, 1985, n° 81; Cherasco, Palazzo Salmatoris, Chagall, Miró, Magritte : La Poesia del Sogno, September-December 2005; Paris, Exhibition Jean Louis Prat-Galerie Lelong, Grand Palais, September-October 2018; Mons, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Mons, Belgium, Exposition Joan Miro : L’essence des choses passées et présentes, October 2022-January 2023, repr. in cat. Literature: Jacques Dupin, Ariane Lelong-Mainaud, Joan Miro : catalogue raisonné, Volume II, 1931-1941, Editions Maeght-Lelong, Paris, 2000; Joan Miró exhibition catalogue, L'essence des choses passées et présentes, Editions BAM, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Mons, Belgium, 2022

Philippe Heim
andré maire
André Maire (Paris, 1898-1984) Vue de Segovie, circa 1940 Oil on canvas 163 x 227 cm Signed lower right Certificate of authenticity issued by Philippe Heim Provenance: the artist's family Literature: André Maire (1898-1984), L'itinéraire décoratif d'un peintre voyageur, Éd. Gallimard, 16 October 2008, repr. p. 89 Exhibition: André Maire (1898-1984), L'itinéraire décoratif d'un peintre voyageur, Roubaix, La Piscine, 18 October 2008 to 1 February 2009















